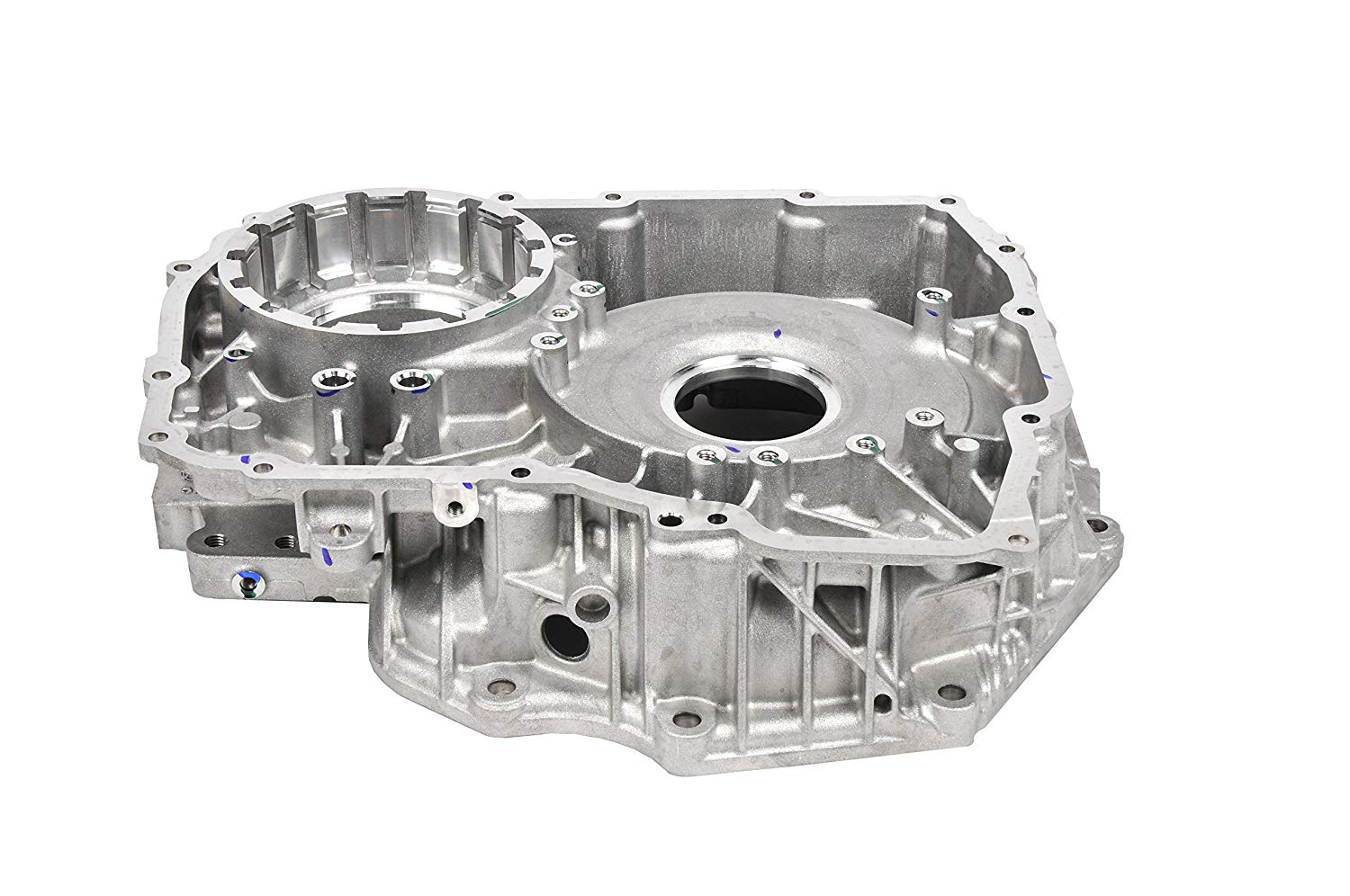
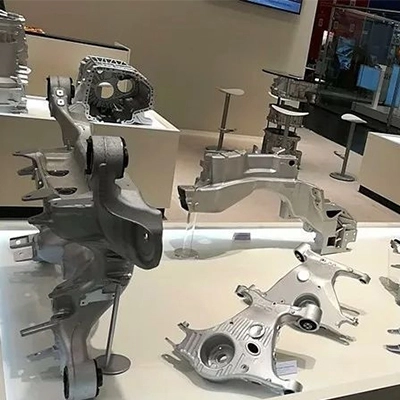
Die-casting mold is one of the three major elements of die-casting production. A die-casting mold with correct and reasonable structure is a prerequisite for the smooth production of die-casting parts, and plays an important role in ensuring the quality of castings (the pass rate of the machine). Due to the characteristics of the die-casting process, the correct selection of various process parameters is the decisive factor for obtaining high-quality castings, and the mold is the prerequisite for the correct selection and adjustment of various process parameters. Die design is essentially a comprehensive reflection of the various factors that may occur in die casting production.
If the mold design is reasonable, there will be fewer problems encountered in actual production, and the casting pass rate will be high. On the contrary, the die-casting mold design is unreasonable. Therefore, when designing the mold, it is necessary to comprehensively analyze the structure of the casting, be familiar with the operation process of the die-casting machine, understand the possibility of adjusting the die-casting machine and process parameters, master the filling characteristics under different conditions, and consider the processing methods of the die-casting mold, Only after drilling and fixing the form can a mold that is practical and meets production requirements be designed.
There are many factors that cause the failure of die casting molds, both external and internal. In actual production, there are three main forms of failure of die-casting molds:
1) Thermal fatigue cracking failure of die casting mold
During the production of die-casting, the die-casting mold is repeatedly subjected to the action of cooling and heating, the molding surface and its interior are deformed, and they are involved in each other, resulting in repeated thermal stress, resulting in damage to the structure and loss of toughness, resulting in the appearance of micro-cracks and continued expansion, once the crack expands, the molten metal squeezes in, and repeated mechanical stress accelerates the crack growth. To this end, on the one hand, the mold must be sufficiently preheated at the beginning of the die casting.
2) Fragmentation failure
Under the action of the injection force, the die-casting mold will crack at the weakest point, especially the scribe marks or electrical machining marks on the molding surface of the die-casting mold are not polished, or the clear corners of the molding will appear first. Microcracks are easy to break when there is a brittle phase at the grain boundary or the grains are coarse. However, the crack spreads rapidly during brittle fracture, which is a very dangerous factor for the chipping failure of the die-casting mold.
3) Corrosion failure
As mentioned earlier, the commonly used die-casting alloys include zinc alloy, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy and copper alloy, as well as pure aluminum die-casting. Zn, Al, and Mg are relatively active metal elements, and they have a good affinity with die-casting mold materials, especially the Al easy-to-bite mold. When the hardness of the die-casting mold is high, the corrosion resistance is better, and if there are soft spots on the molding surface, the corrosion resistance is not good. However, in actual production, the corrosion is only a local part of the die-casting mold. For example, the parts (core, cavity) that are directly eroded by the inner gate are prone to corrosion, and the aluminum alloy is prone to sticking to the mold where the hardness is soft.