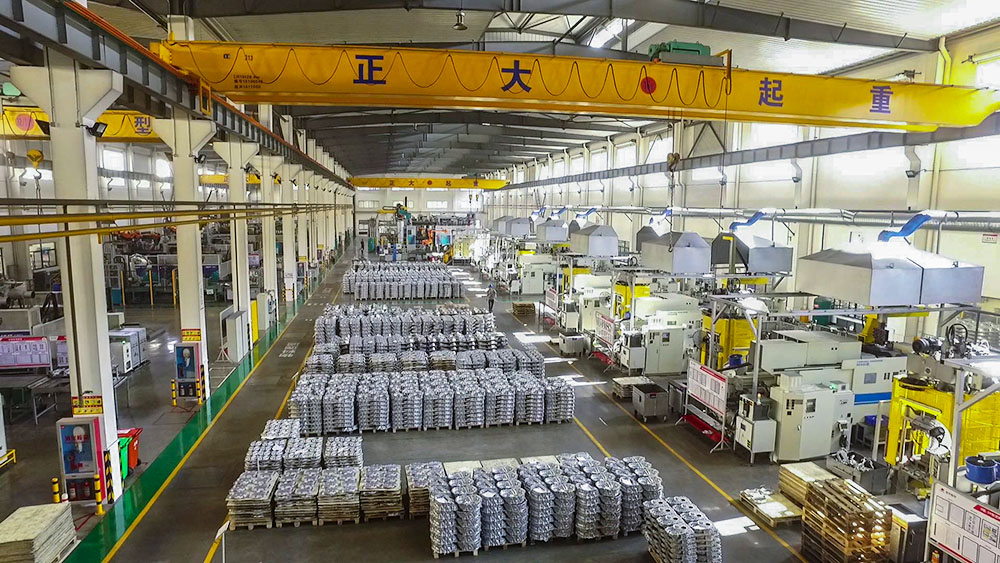
The principle of aluminum alloy heat treatment
Aluminum die-casting heat treatment is to control the heating rate to a temperature and accelerate the cooling. Thereby, the corrosion resistance of the aluminum alloy is improved, the processing ability is improved, and dimensional stability is gained.
Characteristics of aluminum alloy heat treatment
As we all know, steel with high carbon content can obtain high hardness after quenching, but its plasticity is very low. However, after the aluminum alloy is quenching, the strength and hardness of the aluminum alloy will not increase immediately. As for plasticity, it does not decrease but increases. But this kind of quenched alloy, placed for some time (such as 4-6 days and nights), the strength and hardness will increase, and the plasticity will decrease. The phenomenon that the strength and hardness of aluminum alloy increase significantly with time after quenching is called ageing. Aging can occur at room temperature and is called natural ageing. Or it happens in a temperature range (such as 100 to 200°C) higher than room temperature, which is called artificial ageing.
The principle of ageing strengthening of aluminum alloy
The age hardening of aluminum alloy is a complicated process. It depends not only on the composition and ageing process of the alloy but also on the defects caused by the shrinkage of the alloy during the production process, especially the number and distribution of vacancies and dislocations. The current age hardening is the result of the segregation of solute atoms to form a hardened zone.
When the aluminum alloy is quenched and heated, vacancies will form in the alloy. Due to the rapid cooling, these vacancies are too late to be removed and "fixed" in the crystal. The opening in these supersaturated solid solutions combines with solute atoms. The supersaturated solids solution is in an unstable state and transformed into an equilibrium state. It accelerates the diffusion rate of solute atoms, thereby accelerating the segregation of solute atoms.
The size and number of hardened zones depend on the quenching temperature and quenching cooling rate. The higher the quenching temperature, the more concentrated the vacancies, the more the number of sclerosis zones, and the smaller the size. The greater the quenching cooling rate, the more vacancies, which is beneficial to increase the number of sclerosis zones and reduce the size of hardened zones.
One of the characteristics of precipitation hardening alloys is that the equilibrium solid solubility changes with temperature and the solid solubility increases with increasing temperature. Most aluminum alloys meet this condition.