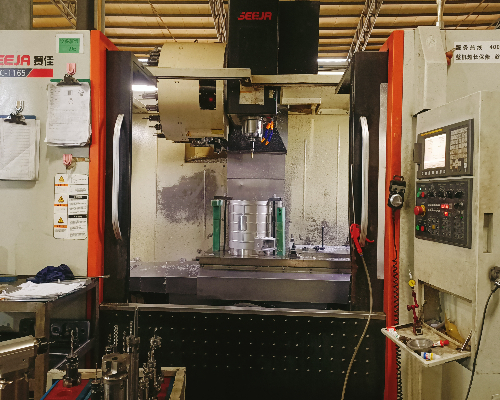

In modern manufacturing, CNC machining and traditional machining represent two distinctly different modes of production, each with its own advantages in precision, efficiency, and technological application. CNC machining, or computer numerical control machining, stands at the forefront of manufacturing technology, automating production through programmed control of machine tools. Traditional machining, on the other hand, relies on the experience and manual operation of craftsmen, emphasizing customization and flexibility.
The greatest hallmark of CNC machining is its high level of accuracy and repeatability. With parameters preset by software, CNC machines can precisely control the path of cutting tools, producing parts that are consistent in size and smooth in finish. This method is particularly suited for the mass production of complex parts in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and high-precision medical equipment. CNC machining also effectively reduces material waste and improves production efficiency, though the investment and maintenance costs for the equipment are higher.
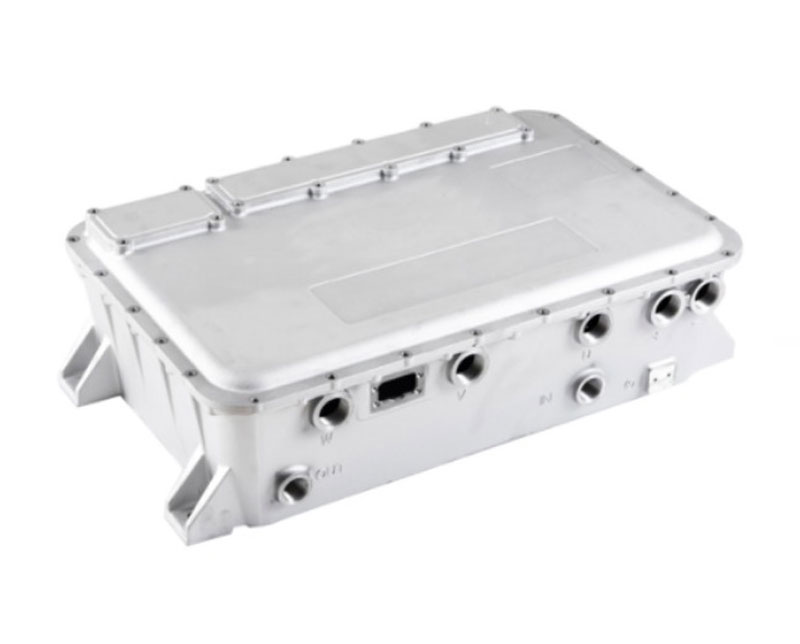
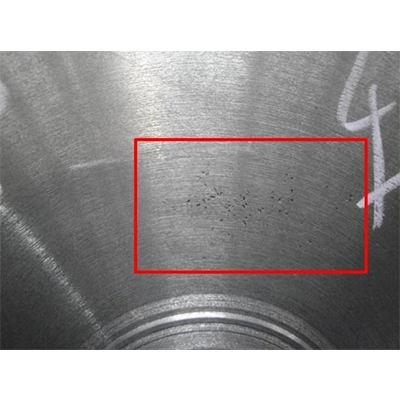
The integration of CNC machining with traditional machining in the manufacturing of automotive aluminum die-cast parts has brought innovation to the industry. The precise control and high efficiency of CNC machining, combined with the flexibility and adaptability of traditional machining, allow even the most complex aluminum die-cast parts to be produced with high quality and low cost. For example, key components such as the engine block, cylinder head, and oil pan of an automobile.
In the future, with the continuous emergence of new materials and processes, CNC machining and traditional machining will continue to play a significant role in the manufacturing of automotive aluminum die-cast parts. Together, they will drive the trend towards lighter and more performant automobiles, meeting the market demand for efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.