
1. Mold Material:
The choice of mold material influences the service life of the mold. According to research, improper material selection and heat treatment can lead to premature mold failure. Aluminum die-casting molds are hot working molds. The manufacturing conditions are relatively strict. The melting point of aluminum is between 580-740°C. During the die casting process, the aluminum temperature needs controlled between 650-720°C and preheated. If it is no preheated, the cavity surface temperature will rise from room temperature to liquid temperature. At this time, the surface of the cavity will bear tensile stress. During the mold opening process, the cavity surface will subject to compressive stress. After frequent die casting, defects such as cracks will appear on the surface of the mold.
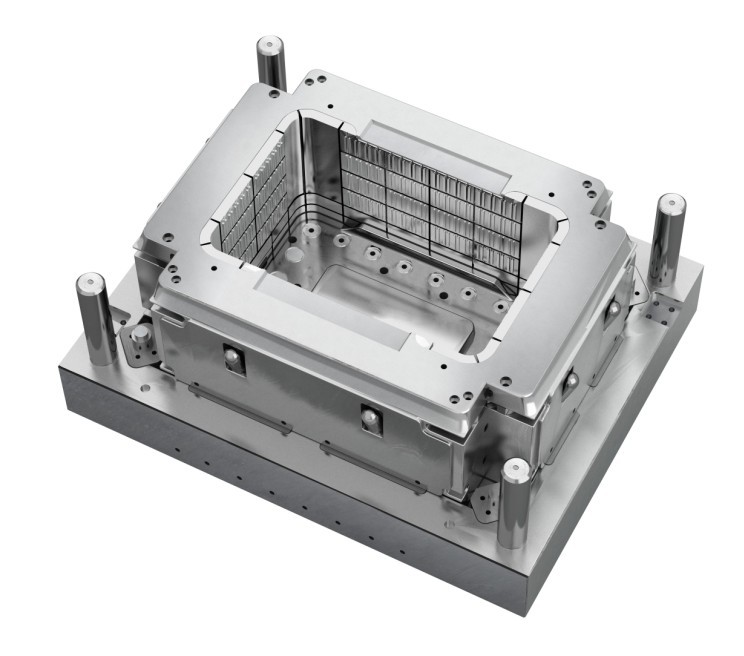
2. Mold Structural design:
When designing aluminum die-casting molds, it is necessary to avoid excessively sharp rounded corners and excessive cross-sectional changes. The stress caused by the fillet is ten times the average stress of the mold, so it is easy to damage the mold. Also, the designer should pay attention to the deformation and cracking of the mold in the subsequent heat treatment. To prevent the formation of the above defects, the cross-sectional dimensions of the mold should be uniform and symmetrical, blind holes should be open through the holes as much as possible, and the processing holes should open. The mold structure design should also avoid the appearance of geometric gaps, including knife marks, included angles, scouring grooves, cavities, and cross-sectional mutations.
3. Mold Machining:
Incorrect processing can easily lead to stress concentration and insufficient finish, which may cause mold defects and affect life. During mold processing, the cooling control system surface should be smooth and free of mechanical marks.



